One way that you can protect your account is by using what is referred to as a “limit order.” These orders specify the most you are willing to buy or sell a security at, making any trade you enter better understood before getting into it. Depending on the situation, you may wish to pay an exact amount, or a better price, for your purchase. It should be noted that if the price isn’t hit, including being “jumped over”, the order may or may not be triggered, depending on whether it is used as protection or simply to enter the market.
Limit orders are instructions given to the broker on behalf of the trader to execute a trade under certain circumstances. A limit order will guarantee that the trader will only buy or sell at a specified price or better.
How Do Limit Orders Work?
A limit order is an order that has a prespecified price to buy or sell a security. For example, if a trader is looking to purchase stock with a limit of $10.50, they will only buy the stock at the price of $10.50 or lower. If the trader were looking to sell those same shares with a limit of $12.50, the trader would not fire off a sell order of any shares until the price is $12.50 or higher.
By using a limit order, the trader is guaranteed to pay the specified prices are better but is not necessarily assured that the order will be filled. A limit order will give the trader more control over the execution price of a trade, especially if they are worried about using a market order during periods of heightened volatility.
- What Is a Sell Limit Order? A sell limit order is a limit order that a trader can use to sell stock at a specific price or perhaps above that particular price. A sell limit order allows an investor to control the selling price with how much they are willing to sell the stock for.
- What Is a Buy Limit Order? A buy limit order allows a trader to specify the price at which they are willing to buy a stock. By placing a buy limit order, you are instructing the broker that you are willing to buy the stock at an exact price. If you cannot get that price, you won’t be buying shares at a worse price.
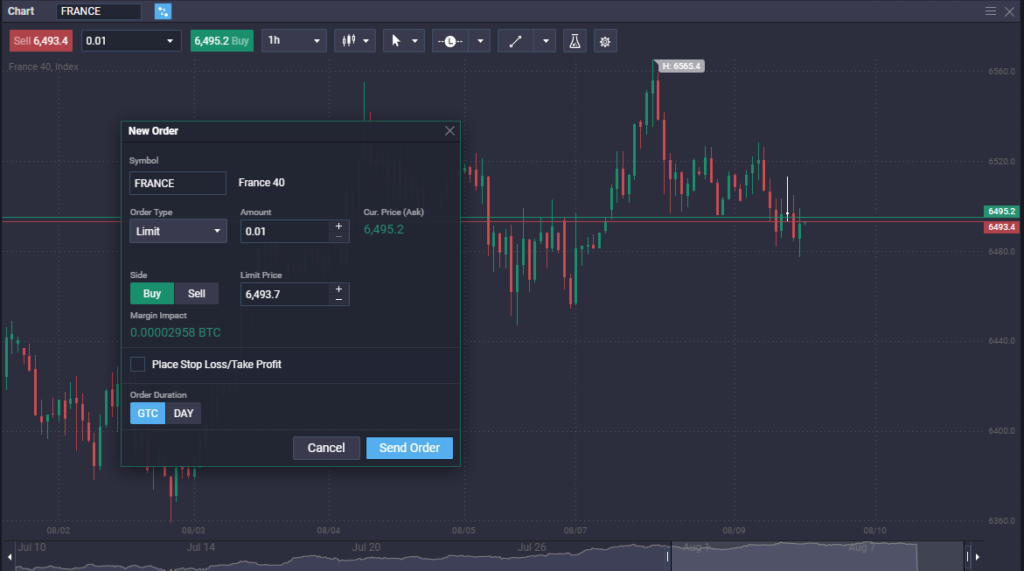
Limit Order Example
A trader wishes to buy American Airlines but believes the price of $21.48 is high. The methodology they believe in says that the cost of AA should be lower but that it should continue to appreciate over time. Because of the trader’s methodology, they feel much more comfortable buying AA at $20.50.
The trader puts in a buy limit order to buy AA at $20.50 and waits to see if the market drops to that level. In one scenario, the trader sees the stock price fall to the $22.50 level, and the order is triggered. Perhaps they even get a bit lucky, and their order gets partially filed just below $22.49. (The order simply states, “I want to buy x amount of AA, and I will not pay more than $20.50 for it.” The trader certainly would not have an issue paying a little less if they can.)
In another scenario, the price of American Airlines doesn’t fall enough to fulfill the trading order. This means that the trader simply will not be buying it. The conditions weren’t met, so the order wasn’t triggered.
How Long Do Limit Orders Last?
Limit orders can last for a bit or as long as you choose. There is no ‘rule’ as to how they have to be placed, but depending on the situation, there are a few general guidelines that traders and platforms tend to stick to.
- Day orders: Day orders last for the trading day. Many brokers use this by default, but not all. Make sure you understand the length of time that the platform will default to. With a day order, the order is deleted at the end of the trading day.
- Good-til-canceled: These orders are prevalent as well. They are left open until they are either filled or the trader decides to cancel them. These orders are typically how CFD platforms will work, as most CFD markets are open 24 hours. Because of this, if you use a “good-til-canceled” order, you need to ensure you do not forget about it because if the price hits your level, you could unknowingly enter the market.
These orders can also be used to stop losses. You want them to trigger. This lets the trader step away from the screen, knowing the platform has a protective order. If your limit price gets jumped, you could see heavier losses. Therefore, a stop loss order is rarely specified as a limit order per se.
- Fill-or-kill: “Fill-or-kill” orders should be thought of as “all or nothing.” This type of order needs to be filled in the entirety of the required quantity, or they are canceled.
- Immediate-or-cancel: These orders are similar to fill-or-kill orders in the sense that they are either processed immediately or are canceled. However, unlike fill-or-kill, they can be partially filled if it is immediately.
What’s a Limit Price in Stocks?
The limit price is the price that the trader sets. It’s the price that a limit order will be executed and assuming that the asset reaches that particular level. Think of it as the price an investor is willing to pay for a stock or sell it for.
- Buy limit orders: The limit price on a buy order is usually placed below the current stock price, and the order will process if the stock price dips down to that level or lower. You can think of this as the price ceiling of the trader’s willingness to pay. Buy limit orders are one of the favorite ways for professionals to protect themselves.
- Sell limit order: The limit price on a sell limit order is usually placed above the current price of the stock and will process at that set price or higher. You can think of this as the price floor of the trader’s willingness to execute.
Limit Order vs. Market Order
While limit and market orders are the two most common types of orders, they are vastly different in their execution. The market order tells the broker that the trader wants to buy or sell an asset at the best price. Market orders are executed immediately, regardless of the available price. They are vulnerable to slippage when the price moves quickly enough to make your order execute far from the original price. This is especially true in fast-moving markets.
For example, you decide to place a buy order for Ethereum at $1325. You place a market order to do so, but the market price is moving quickly. The cost of Ethereum continues to rise rapidly, and you get a price above $1325. Depending on the market conditions, it can be a substantial difference.
With the same scenario, the trader could have put in a buy limit order to buy Ethereum at $1325. The price moved so fast that they didn’t get their order filled. The limit order did its job – it kept the trader from paying more than they wanted. Some platforms allow for “variation” of the order. Perhaps you are okay with paying up to $5 extra for this order. In that case, your order could have been filled at, say, $1327.34 as it was within the tolerance of the order.
Limit Orders vs. Stop Orders
A stop order is a bit different than a limit order and can be a stop-loss order or a stop-limit order. Both types of stop orders are orders that are used to protect from seeing losses get out of hand. They instruct the broker to get out of the market if the price of an asset moves against you.
A stop-loss order will specify a certain level of price that will trigger the sale of an asset or, in the case of a short position, the buying back of that asset. This is to protect the account from experiencing worse losses than necessary. This is essentially where the trader tells the broker, “Get me out at the best price available.”
The stop-limit order works similarly, but only when the asset price hits a certain amount. Sometimes, the broker will allow you two levels to execute within, meaning there is some tolerance for slippage or the move against you getting worse to ensure you get out of a losing trade. However, if the market is moving too fast and the broker can’t follow the tolerance, you will not have the order executed. This can be a dangerous thing in the wrong environment.
Why Use a Limit Order?
Below are some of the most common reasons you would use a limit order. While the reasons are numerous, these are the most often cited:
- Control the price executed: The most common reason to use a limit order is to control the price at which the order is executed. Knowing the price ahead of time gives you more control of the trade.
- Price improvement: Another reason traders will use a limit order is that they can sometimes get price improvement. Remember, when you set a limit price, you’re willing to execute that price or better.
- Only trade when conditions are met: Some people use limit orders to ensure they get a “discount” on current pricing. For example, some systems suggest that a 1% drop offers a bit of value you can take advantage of. By using a limit order, you can preplan the setups.
What Are the Downsides to a Limit Order?
Although there are quite a few advantages to using a limit order, there are also some downsides. You should be aware of a few things:
- Doesn’t guarantee execution: A limit order does not guarantee execution. Execution will only occur when a specific price is traded. You may lose your chance at an opportunity.
- First come, first served: Keep in mind that you have to have shares available at that price. For example, if thousands of shares are ordered before you put in your order, those shares may not be available by the time your turn comes in the queue.
How to Place a Limit Order
Typically, it is quickly done by the same dialog box that you would use to place any trade on your platform. If you are ready to place a trade, you typically need to change a dialog box from “market order” to “pending order.” After that, you choose “limit order.” At this point, you need to place the appropriate price at which you are willing to execute your position. Any appropriate stop-loss order should also be mentioned in this transaction as well, and the broker will then simply wait to see whether or not the proper conditions get reached.
Conclusion
Limit orders are a great way to ensure you do not get filled at a less advantageous price. After all, the market can be very volatile at times, and using buy limit orders and sell limit orders might be the best way to mitigate some of the issues you can run into. After all, sometimes the market gets into a runaway mode, and the worst thing you can do is jump into the market with a “market order” and get filled at a horrible price.
However, they are not necessarily helpful when it comes to protecting your account because if you have a limit order being used as a stop order, the price can jump over your trigger price, perhaps leaving you exposed. In that situation, you are looking at the need for a stop-loss order. Jumping into a market with a “market order” is a very amateurish way of trading.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the point of a limit order? Know ahead of time what price you will pay for an asset. For example, you can decide to enter a buy order of $23,100 for Bitcoin, 1.2134 for GBP/USD, or $9.01 for US Steel. By using these orders, you can determine your cost basis. Sometimes, the broker can even fill your order for a better price than the one requested.
- Are limit orders a good Idea? Yes, in general. This lets you know the price you will pay for something before purchasing it. Otherwise, if you enter via a market order, you can get a worse price than you initially thought. It doesn’t matter if it is a buy order or a sell order, they can help improve the price.
- What is an example of a limit order? A trader wants to buy stock XYZ at $14. The limit order to buy 100 shares of XYZ for $14 will not get triggered unless they can get those shares at that price or lower. They will not fill at the current market price, nor will they fill at any price above $14.
- How long do limit orders last? This depends on the trader. They can last for the remainder of the trading session or until canceled.
- Which is better: stop or limit order? When buying an asset, the limit order ensures you get the price you want or better. However, limit orders can be a disaster if the actual price isn’t hit. This can cause a position to move against you even further as the conditional price wasn’t triggered. You can use what is known as a “stop-limit” order to protect against this.
- Why isn't my limit order selling? There are a couple of possible reasons. The first is that the price “jumped over” the trigger price, and the other is that there were orders ahead of you in the queue. If there wasn’t enough supply of volume at that price level, you might have been left out.
- What is the primary disadvantage of a limit order? The primary disadvantage of using a limit order is that they don’t always get filled. The exact price needs to be hit.
- Can you cancel the limit order after hours? Most brokers will allow the cancellation of orders, even after hours. However, not all do, so ensure you understand the parameters you are working with.
- Will my limit order be executed after hours? It can be at the broker's discretion, but most brokerages will allow these orders to be filled outside of regular business hours.
- What happens if a limit order is not executed? This depends on the type of limit order you have chosen. If it is a “day order,” then at the end of the trading session. If it is a “good-til-canceled” order, it remains open and can be triggered later.











